Election Science: Combining Theory and Practice
Election science is an interdisciplinary field that focuses on the design, conduct, and administration of elections. Unlike political science, it doesn't involve studying public opinion or forecasting election outcomes. Instead, election science combines social choice theory (from mathematics and economics) with empirical research on election administration (from political science).
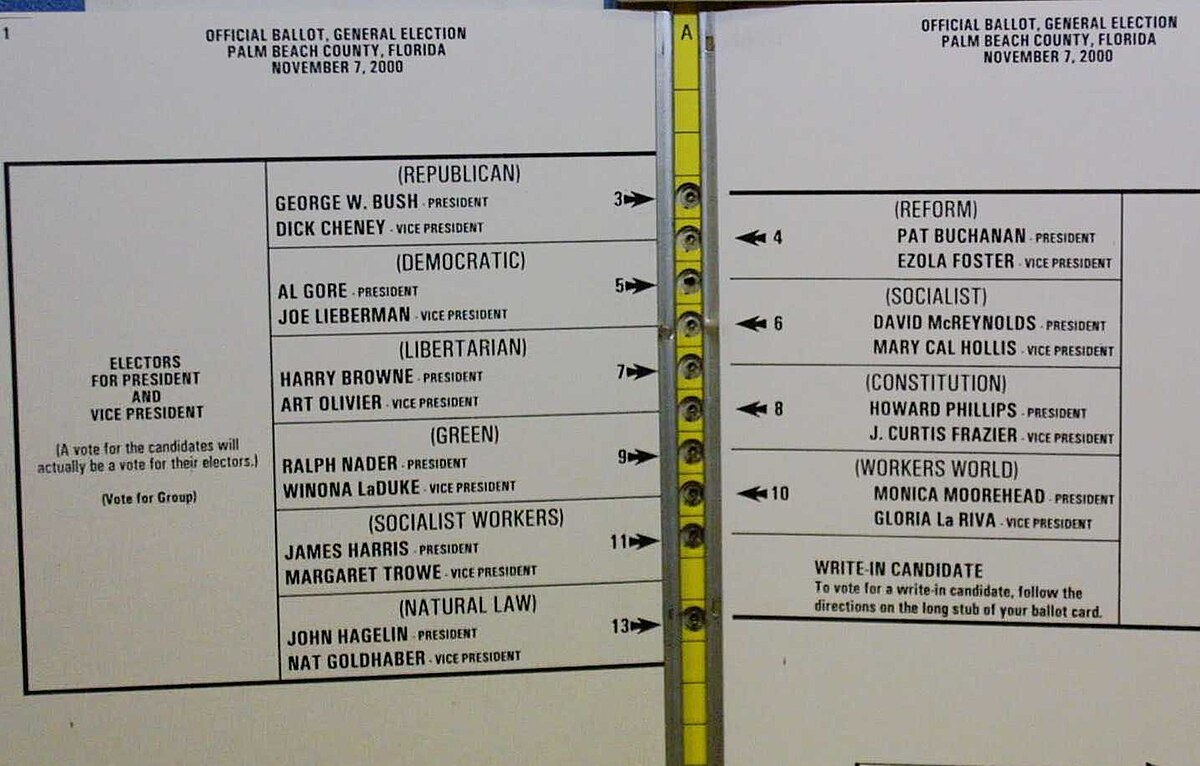
The roots of election science lie in the study of electoral systems, particularly the development of social choice theory in the 18th century. It gained prominence after the contentious 2000 US presidential election, highlighting the need for improved election administration. Key areas of study in election science include gerrymandering, electoral fraud, suffrage, and voter registration.
Academic institutions and organizations play an important role in election science. There are dedicated academic conferences and sub-conferences within larger political science organizations. Additionally, universities offer degree programs in political science with a data science track. The Center for Election Science fosters research and education in this field.
Key Points:
- Election science combines social choice theory and election administration research.
- It emerged in response to the 2000 US presidential election.
- Subjects of study include gerrymandering, electoral fraud, and voter registration.
- Academic institutions and organizations support election science research and education.
- The field aims to improve the design and administration of elections.