Geography
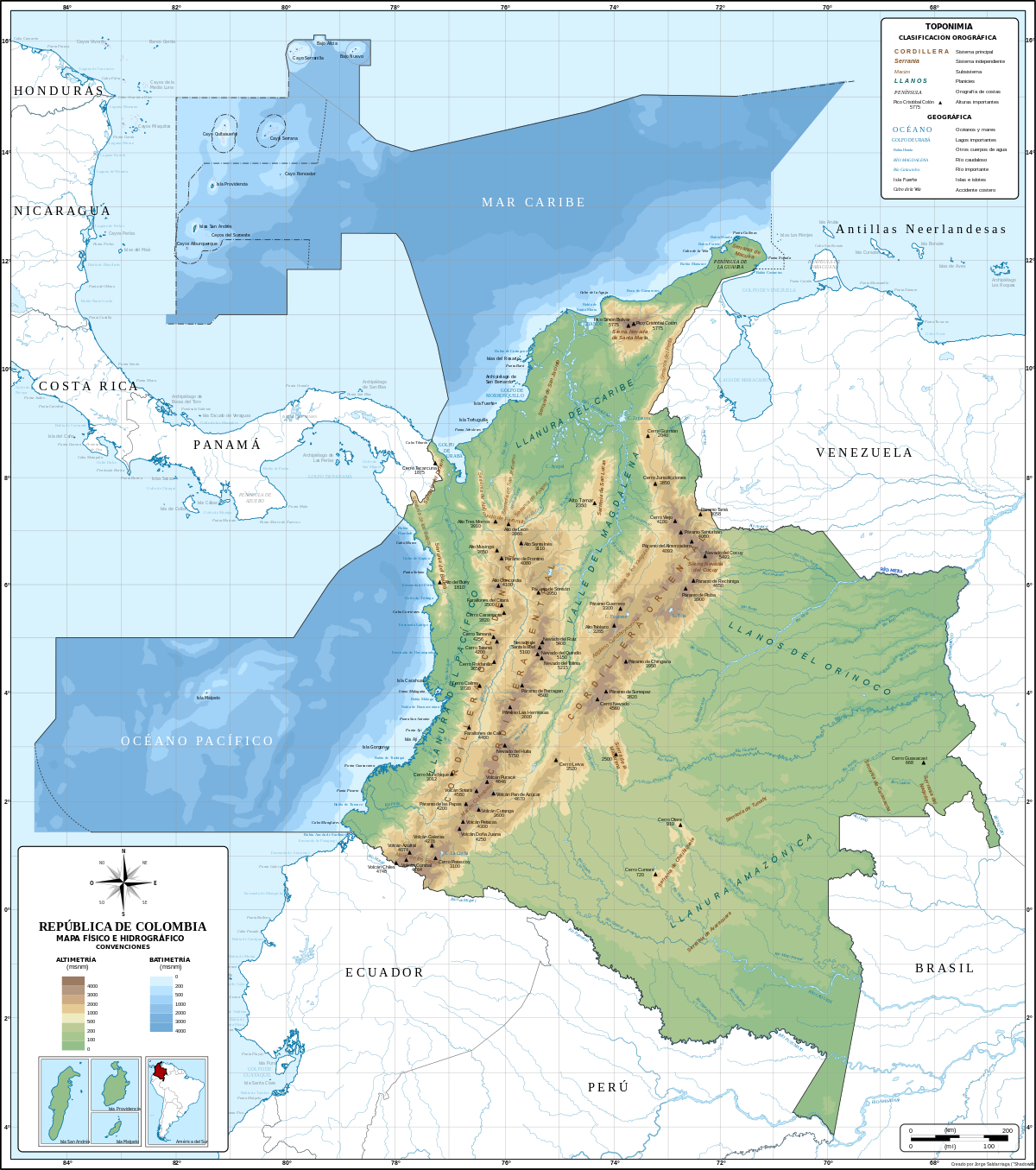
Colombia is located in northwestern South America, with territories extending into Central America. It borders Panama, Brazil, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru. The country's land area of 1,141,748 km² makes it the 25th largest nation globally and the fourth largest in South America.
Colombia can be divided into five natural regions: the Andes, Pacific Ocean coastal region, Caribbean Sea coastal region, Llanos (plains), and Amazon Rainforest. The Andes, a mountain range shared with Ecuador and Venezuela, is the defining geographical feature. The Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea coastal regions are separated by swamps at the base of the Isthmus of Panama, and the Llanos cover nearly 60% of the country's land area in the east.
Andean Region
The Andes mountains divide into three distinct ranges in Colombia: the Western Cordillera, Central Cordillera, and Eastern Cordillera. The Western Cordillera is relatively low, while the Central Cordillera is the loftiest and contains snow-capped volcanoes. The Eastern Cordillera differs from the others in that it contains several large basins.
The Magdalena River Valley, formed by the convergence of the Western and Central Cordilleras, is an important agricultural region. The Cauca Valley, between the Central and Western Cordilleras, is a deep rift. The Cordillera Oriental hosts the Nevado del Huila, Colombia's highest peak at 17,602 ft above sea level.
Caribbean Region
The Caribbean lowlands include the Guajira Peninsula, the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, and the coastal cities of Cartagena, Barranquilla, and Santa Marta. This region is home to banana and cotton plantations and accounts for approximately 17% of the country's population.
Pacific Region
The Pacific lowlands are the most geographically complex region, featuring narrow coastal plains, the Serranía de Baudó mountain range, and the Atrato Swamp, considered an engineering challenge for the Pan-American Highway.
Orinoquía Region
The eastern plains, or Orinoquía, cover about 699,300 square kilometers. Cattle raising is practiced in the open plains near the Cordillera Oriental, and the Serranía de la Macarena, an outlier of the Andes, has unique vegetation and wildlife.
Amazon Region
The Amazon Basin umfasst zahlreiche große Flüsse, die in den Orinoco oder den Amazonas münden. Der Río Guaviare teilt den östlichen Teil Kolumbiens in die nördlichen Llanos und die südlichen Regenwälder.
Climate
Colombia's diverse climate is primarily influenced by elevation. Temperatures range from hot at sea level to cold at higher elevations, but there is little seasonal variation. Rainfall varies depending on the region, with the Pacific lowlands and parts of eastern Colombia receiving the highest precipitation.
Vegetation
Altitude greatly influences vegetation. The tropical lowlands are home to crops like bananas and coffee, while temperate and cold zones support wheat, potatoes, and forests. Treeless grasslands known as páramos dominate alpine areas, and permanent snow and ice are found at the highest elevations.
Natural Resources
Colombia possesses abundant natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, gold, silver, copper, emeralds, and hydropower potential.
Environmental Issues
Deforestation, soil and water pollution, and air pollution are significant environmental concerns. The ongoing armed conflict has caused long-term environmental damage due to oil pipeline attacks and the destruction of forests for illicit crop cultivation.