Geography
English
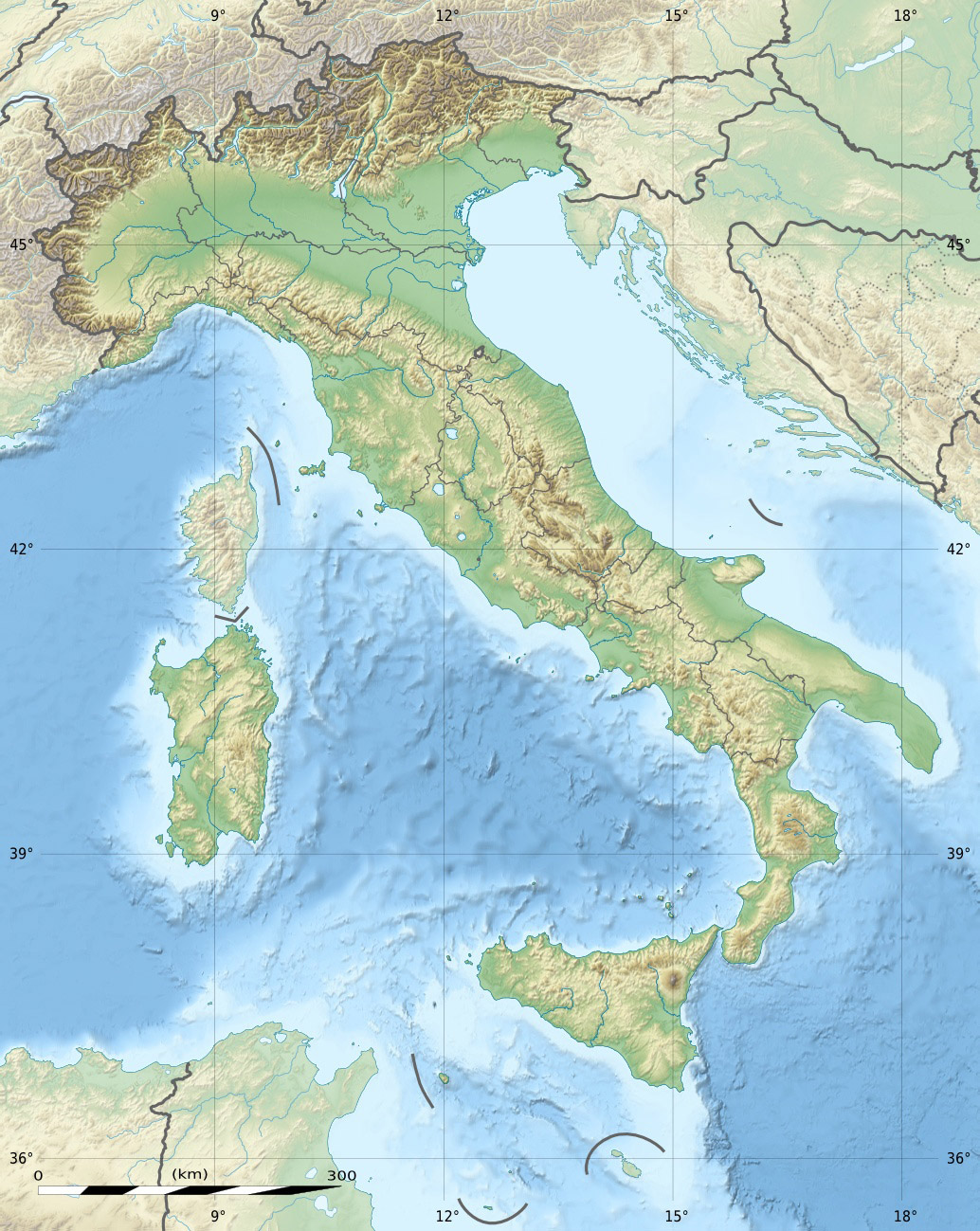
Geography of Italy
Location, Area, and Boundaries:
- Italy occupies the southern part of Europe and the long, boot-shaped Italian Peninsula.
- Total area: 301,230 km² (116,310 sq mi)
- Borders Switzerland, France, Austria, and Slovenia.
Topography:
- Mountains: Alps (northern boundary), Apennines (backbone of the peninsula)
- Hills: Cover most of the territory, alternating with valleys and hollows
- Plains: Largest is the Po Valley, formed by the Po River in northern Italy
Hydrography:
- Rivers: Po (longest), Adige, Tiber
- Lakes: Subalpine lakes (e.g., Garda, Maggiore) in the north; others include volcanic, coastal, and man-made lakes
- Seas and Coasts: Overlooks the Mediterranean Sea, which divides into several seas surrounding Italy; coastline of approximately 7,900 km (4,900 mi)
Other Features:
- Islands: Sicily and Sardinia are the largest; also numerous smaller islands
- Volcanic activity: Italy has numerous active and extinct volcanoes, including Vesuvius and Etna
- Earthquakes: Italy is prone to earthquakes due to its location between tectonic plates
General Characteristics:
- Italy is a peninsula surrounded by water, except to the north.
- The Apennines divide the country into two slopes: the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Sea sides.
- The Italian peninsula is located at the center of the Mediterranean Sea, between the Balkans and the Iberian Peninsula.
- The soil is mainly mountainous, hilly, or volcanic.
- The highest point is Mont Blanc (4,810.90 meters), while the lowest point is Jolanda di Savoia (-3.44 meters).
Orography:
- Mountains cover almost 40% of Italy, with the Alps to the north and the Apennines forming the backbone of the peninsula.
- Notable mountains include Monte Cervino (Matterhorn), Monte Rosa, Gran Paradiso, and the Dolomites.
- Hills, such as the Langhe and Murge, have moderate slopes and alternate with valleys and hollows.
- Plains, including the Po Valley, account for 23.2% of the territory and are mainly formed by river deposits.